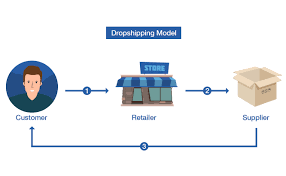
Drop shipping is a form of retail business in which the seller accepts customer orders without keeping stock on hand. Instead, in one form of supply chain management, the seller sends orders and their shipment details to either a manufacturer, wholesaler, other retailer, or a fulfillment house, which then ships the goods directly to the customer. . Is
The seller is responsible for marketing and selling the product, but has limited control over product quality, storage, inventory management, or shipping.[1] By doing so, it eliminates the costs of maintaining warehouses. . – or even a storefront – employs the staff necessary to purchase and store inventory, and similar operations. As with any other form of retailing, the seller makes a profit on the difference between the wholesale and retail price of an item, less any associated sales, merchant, or shipping fees charged against it.
Drop shipping has become a popular business model because it requires minimal initial investment and overhead costs. A drop shipping operation can be managed from any location with an internet connection. However, drop shipping also has its drawbacks, including lower profit margins, less control over the quality of products sold and an increased risk of shipping delays or supply chain problems.[2]
Amazon, the online shopping giant, found early success with a drop-shipping business model where they could offer customers over a million different books while only keeping 2,000 of the most popular titles in stock. Publishers and wholesalers will receive forward orders from Amazon and ship the products directly to the customer using packaging from Amazon.